Press Release
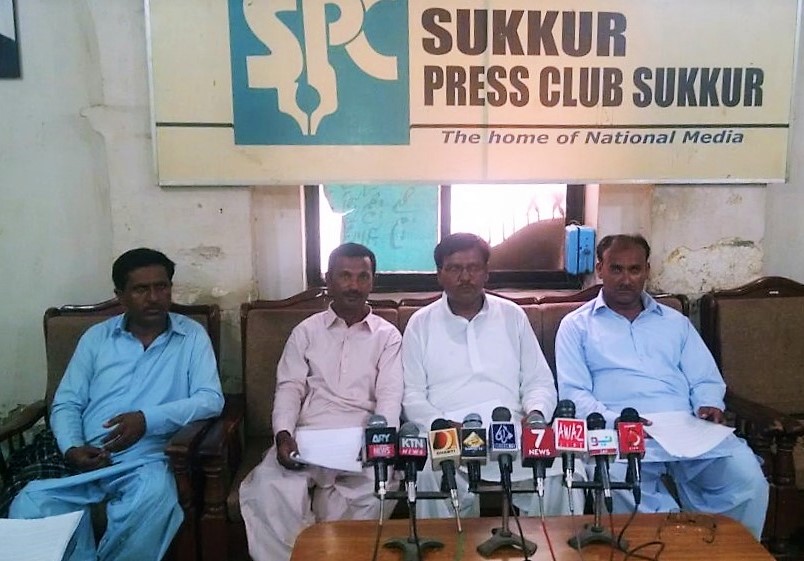

During the press conference PKMT national coordinator Raja Mujeeb, provincial coordinator sindh Ali Nawaz Jalbani, national core group member Hakim Gul and district coordinator ghotki Ali Gohar speaking to the media.
August 12, 2016
The Standing Committee on National Food Security and Research (NFS&R) on August 9, 2016 approved the ‘Plant Breeders Bill 2016’ which had earlier in the year already been approved by the Senate Standing Committee on Cabinet Division; the draft bill will be now be presented before the National Assembly for approval.
Implementation of the Plant Breeders Rights Bill, like the Amended Seed Act, 2015 is dictated by the World Trade Organization (WTO) under the Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual property rights (TRIPS) Agreement. The TRIPs agreement makes it mandatory for the government to provide intellectual property rights (IPRs) on new varieties of plants and seeds. In essence, the Plant Breeders Right’s Act provides monopolistic control to IPR holders of the new varieties of plants or seed prohibiting their use and sale to all others without permission.
The Plant Breeders Act’s is delivered through an ‘effective’ sui generis system or through patents or a combination of both and thus provides mechanisms for plant variety owner to seek IPRs over their plant varieties in each country where they want commercial use of the variety.
The Plant Breeder Right Act basically takes away a centuries old right of farmers to saving and exchanging seed. With gigantic seed corporations such as Monsanto and Syngenta holding intellectual property rights over seeds, the country will on one hand, face serious food insecurity and on the other, loose its sovereignty allowing transnational corporations to dictate food and agricultural production in the country. The royalties paid for IPRs will result in massive seed prices, and farmers already reeling under the steeply rising production costs will face further impoverishment. There is no doubt that the approval of this Bill is equivalent to pushing farmers out of the agricultural sector, reducing them to the status of beggars, a life of misery and humiliation.
Genetically modified seeds (GMOs) are based on genetic engineering (GE) of living organisms including seed and animals and is against evolution of life in nature; the commodification of nature, environmental pollution and further destruction of biodiversity through GMOs is a threat to the entire humanity and goes far beyond ethical dictates of society. It is due to the above reasons and potential health risks associated to GMOs that many countries across the globe have banned GM seed and crops.
Some members of the Standing Committee on NFS&R have shown strong reservations against the bill. According to them, the while the Bio Safety Committee under the Ministry of Climate Change has been given the responsibility for issuing certification on GMOs but lacks expertise on this matter. Pakistan has not undertaken any research and analysis on GE crops and their impacts, which is absolutely against international law on this issue.
Based on the above, Pakistan Kissan Mazdoor Tehreek, an alliance of small and landless farmers and Roots for Equity strongly reject the Plant Breeders Rights Bill demanding first, a complete elimination of the role of foreign seed companies in agricultural production and second, any further decision making in this context to be based on inclusion and decision making role of farmers’ organizations.
Released by Pakistan Kissan Mazdoor Tehreek (PKMT)
Urdu Press Release